Where missions come alive
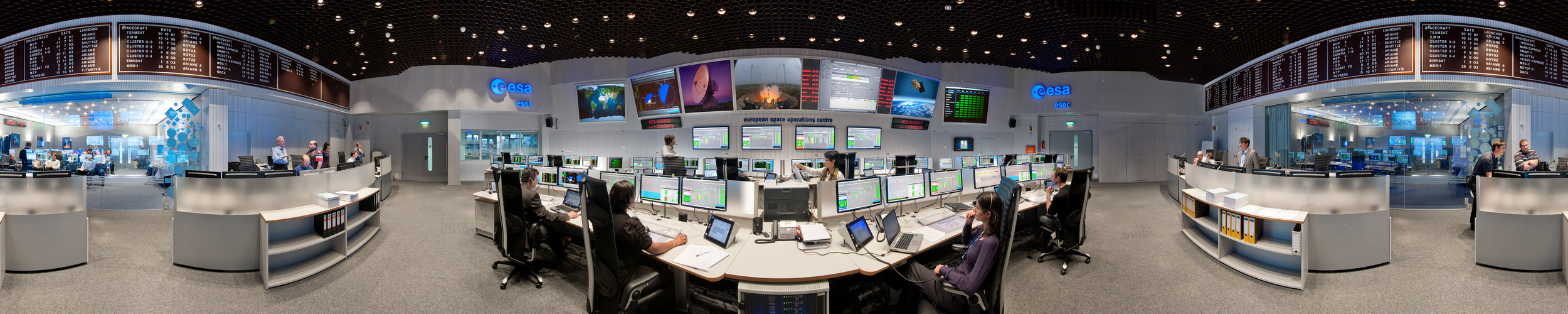


Step inside ESA's Main Control Room at the Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany
Photo credit: ESA/J. Mai
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2


Step inside ESA's Main Control Room at the Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany
Photo credit: ESA/J. Mai
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2
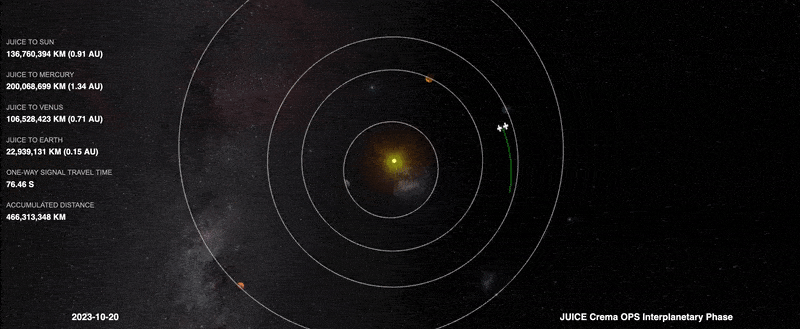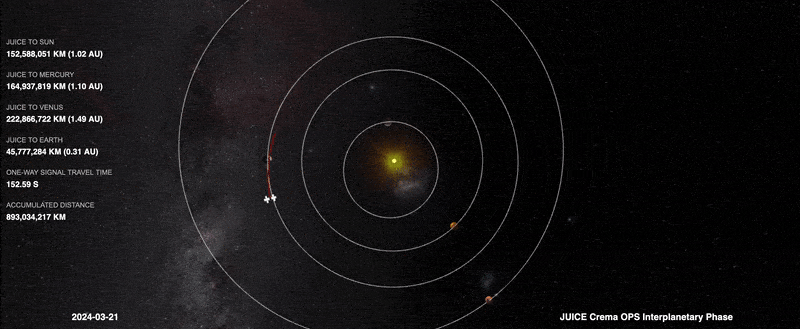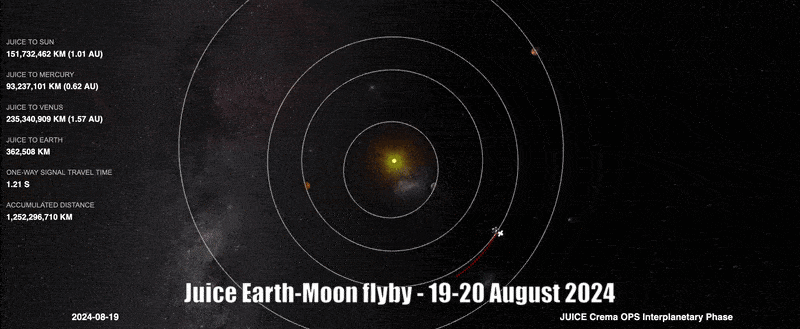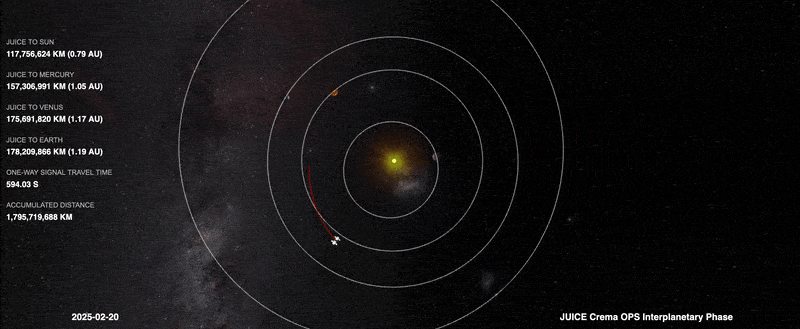
 Image: Juice manouevre lines it up for 2024 Earth-Moon flyby
Image: Juice manouevre lines it up for 2024 Earth-Moon flyby
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2
The CIA was founded in the wake of the 1947 National Security Act. The Act foresaw no need for the Courts and Congress to oversee a simple information-aggregation facility, and therefore subordinated it exclusively to the President, through the National Security Council he controls.
Within a year, the young agency had already slipped the leash of its intended role of intelligence collection and analysis to establish a covert operations division. Within a decade, the CIA was directing the coverage of American news organizations, overthrowing democratically elected governments (at times merely to benefit a favored corporation), establishing propaganda outfits to manipulate public sentiment, launching a long-running series of mind-control experiments on unwitting human subjects (purportedly contributing to the creation of the Unabomber), and—gasp—interfering with foreign elections. From there, it was a short hop to wiretapping journalists and compiling files on Americans who opposed its wars.
https://edwardsnowden.substack.com/p/americas-open-wound
#Snowden #CIA #covert #operations #foreign #elections #wiretapping #journalists

 Image: Lagrange Points
Image: Lagrange Points
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2
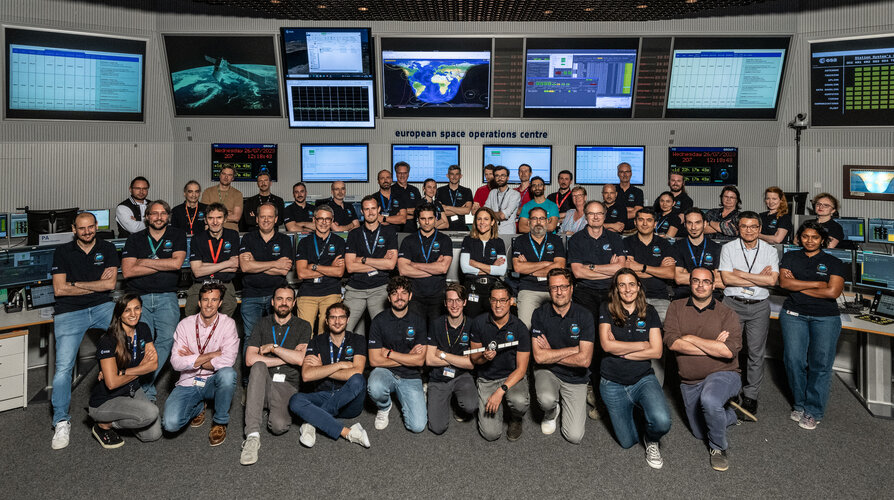

 Image: Aeolus mission control team wraps up successful operations in first-of-a-kind assisted reentry
Image: Aeolus mission control team wraps up successful operations in first-of-a-kind assisted reentry
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2

 Video: 00:05:00
Video: 00:05:00
ESA’s wind mission Aeolus is coming home. After five years of improving weather forecasts, the satellite will return in a first-of-its-kind assisted reentry. At ESA’s Space Operations Centre in Germany, mission control will use the satellite’s remaining fuel to steer Aeolus during its return to Earth.
Find out more about the mission, its successes and how Aeolus is paving the way for safe reentries.
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2

 Video: 00:13:21
Video: 00:13:21
Satellites in orbit underpin our modern lives. They are used in many areas and disciplines, including space science, Earth observation, meteorology, climate research, telecommunication, navigation and human space exploration. However, as space activities have increased, a new and unexpected hazard has started to emerge: space debris.
If space debris – uncontrolled human-made objects such as spent upper stages of rockets and pieces of satellites – hits a satellite, it could cause serious damage, which can even end a mission (as has happened in the past). If debris crashes on Earth’s surface, it could potentially hit populated areas.
In this second video, Nicolas looks back on the first key steps taken at ESA to develop the Space Safety Programme, devoted to the detection, prevention and mitigation of threats originating from space. This includes not just space debris but also asteroids and space weather. The latter is an intense, occasional energetic storm of particles and material emitted by the Sun. Mitigating these hazards protects our planet, society and economically-important infrastructure on Earth and in orbit.
A key element for the forecasting and prevention of space weather is to observe the Sun from the side. Discover more in this second video of the ESA Masterclass with Nicolas Bobrinsky. With 35 years of experience at ESA, Nicolas Bobrinsky is the former Head of Ground Systems Engineering & Innovation Department. He initiated and further managed the Space Situational Awareness and later the ESA Space Safety Programme.
In four episodes of this new series of ESA Masterclass, Nicolas takes us through major events in his career at ESA, covering cornerstone missions, first attempts, overcoming technical challenges, leading diverse teams and solving the unexpected problems that are part of any space endeavour.
Access all episodes of ESA Masterclass with Nicolas Brobinsky.
Access all ESA Masterclass videos.
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2


For one hour on Friday 2 June, join ESA on YouTube for a space first as live images stream down direct from Mars – this will be the closest you can get to a live view from the Red Planet.
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2
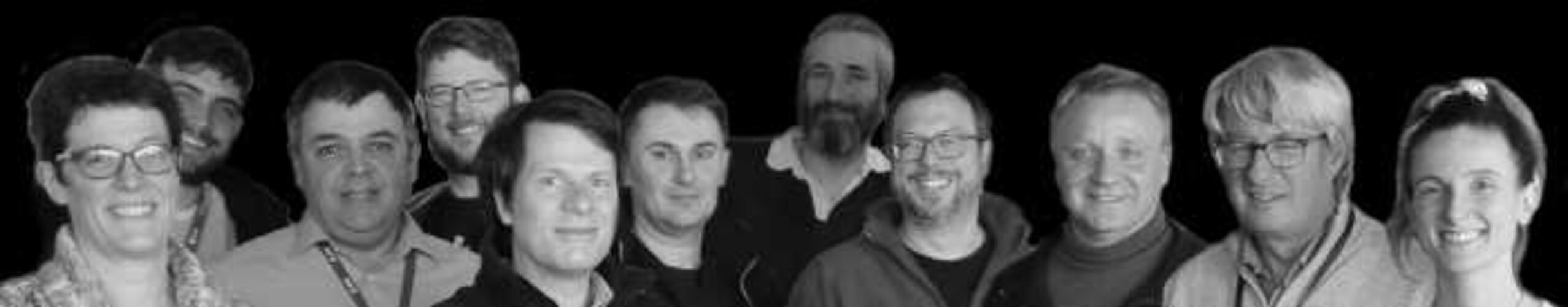

 Image:
Image:
A mysterious signal is being sent by ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter on 24 May, a spacecraft orbiting the Red Planet looking for evidence of possible biological or geological activity.
As part of the global 'A Sign In Space' art project, it will strike huge antennas dotted around the globe; the Green Bank Telescope (West Virginia), the Medicina Radio Astronomical Station (Italy) and the Allen Telescope Array (California).
Early tests were conducted to ensure the feasibility of the endeavour and allow the ground-based observatories to fine tune their systems to be ready for the public event.
During preparations for sending the ‘alien’ message, the Flight Control Team prepared their own special message – a picture of the team beamed down on 14 March, TGO’s 7th launch anniversary
The message was first sent up to the spacecraft from ESA’s mission control centre in Darmstadt, Germany, on 10 May. It was stored onto its memory, converted into ‘telemetry’ (data) and will this evening be beamed back down to Earth.
#operations #space #science #esa #europeanspaceagency
posted by pod_feeder_v2