FSF Blogs: FSD meeting recap 2024 12 06
Check out the important work our volunteers accomplished at today's Free Software Directory (FSD) IRC meeting.
Check out the important work our volunteers accomplished at today's Free Software Directory (FSD) IRC meeting.
Eleven new GNU releases in the last month (as of November 29, 2024):
Welcome to the Free Software Supporter, the Free Software Foundation's (FSF) monthly news digest and action update -- being read by you and 231,349 other activists.
The Licensing and Compliance Lab has been diligently serving the free software community.
Join the FSF and friends on Friday, December 6 from 12:00 to 15:00 EST (17:00 to 20:00 UTC) to help improve the Free Software Directory.
1 December 2024 Unifont 16.0.02 is now available. This is a minor release with many glyph improvements. See the ChangeLog file for details.
Download this release from GNU server mirrors at:
https://ftpmirror.gnu.org/unifont/unifont-16.0.02/
or if that fails,
https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/unifont/unifont-16.0.02/
or, as a last resort,
ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/unifont/unifont-16.0.02/
These files are also available on the unifoundry.com website:
https://unifoundry.com/pub/unifont/unifont-16.0.02/
Font files are in the subdirectory
https://unifoundry.com/pub/unifont/unifont-16.0.02/font-builds/
A more detailed description of font changes is available at
https://unifoundry.com/unifont/index.html
and of utility program changes at
https://unifoundry.com/unifont/unifont-utilities.html
Information about Hangul modifications is at
https://unifoundry.com/hangul/index.html
and
We received a grant from NLnet foundation to pay for the development of libeufin for regional- and event-currencies. NGI assists these projects by paying for independent security audits. Thus, we are happy that RadicallyOpenSecurity performed an external crystal-box security audit of the libeufin component of GNU Taler. You can find the final report here. We already addressed all significant findings and compiled a response detailing the changes. We thank RadicallyOpenSecurity for their work, and NLnet and the European Commission's Horizion 2020 NGI initiative for funding this work.
Check out the important work our volunteers accomplished at today's Free Software Directory (FSD) IRC meeting.
i686 users will probably be unable to upgrade, due to a problem with the latest archlinux32-keyring 20241114-1
the solution is posted on the bug tracker https://labs.parabola.nu/issues/3679
An Austrian petitioner succeeded in realizing what the US government failed to see: that free software is vital for the infrastructure of a free society.
A lot has happened with respect to the Hurd since our Childhurds and GNU/Hurd Substitutes post. As long as two years ago some of you have been asking for a progress update and although there have been rumours on a new blog post for over a year, we were kind of waiting for the rumoured x86_64 support.
With all the exciting progress on the Hurd coming available after the recent (last?) merger of core-updates we thought it better not to wait any longer. So here is a short overview of our Hurd work over the past years:
Update Hurd to 3ff7053, gnumach 1.8+git20220827, and fix build failures,
Initial rumpdisk support, more on this below, which needed to wait for:
A libc specific to Hurd, updating gnumach to 1.8+git20221224 and hurd to 0.9.git20230216,
Some 40 native package build fixes for the Hurd so that all development dependencies of the guix package are now available,
A hack to use Git source in commencement to update and fix cross build and native build for the Hurd,
Support for buiding guix natively on the Hurd by splitting the build into more steps for 32-bit hosts
Even nicer offloading support for Childhurds by introducing Smart Hurdloading so that now both the Bordeaux and Berlin build farms build packages for i586-gnu,
Locale fixes for wrong glibc-utf8-locales package used on GNU/Hurd,
More locale fixes to use glibc-utf8-locales/hurd in %standard-patch-inputs,
And even more locale fixes for using the right locales on GNU/Hurd,
A new glibc 2.38 allowing us to do (define-public glibc/hurd glibc)—i.e., once again use the same glibc for Linux and Hurd alike, and: Better Hurd support!,
Creation of hurd-team branch with build fixes, updating gnumach to 1.8+git20230410 and hurd to 0.9.git20231217,
A constructive meeting with sixteen people during the Guix Days just before FOSDEM '24 with notes that contain some nice ideas,
Another new glibc 2.39; even better Hurd support, opening the door to x86_64 support,
Yet another restoring of i586-gnu (32-bit GNU/Hurd) support,
The installer just learnt about the Hurd! More on this below, and finally,
Another set of updates: gnumach (1.8+git20240714), mig (1.8+git20231217), hurd (0.9.git20240714), netdde (c0ef248d), rumpkernel (f1ffd640), and initial support for x86_64-gnu, aka the 64bit Hurd.
Back in 2020, Ricardo Wurmus added the NetDDE package that provides Linux 2.6 network drivers. At the time we didn't get to integrate and use it though and meanwhile it bitrotted.
After we resurrected the NetDDE build, and with kind help of the Hurd developers we finally managed to support NetDDE for the Hurd.. This allows the usage of the Intel 82573L Gigabit Ethernet Controller of the Thinkpad X60 (and many other network cards, possibly even WIFI). Instead of using the builtin kernel driver in GNU Mach, it would be running as a userland driver.
What sparked this development was upstream's NetBSD rumpdisk support that would allow using modern hard disks such as SSDs, again running as a userland driver. Hard disk support builtin in GNU Mach was once considered to be a nice hack but it only supported disks up to 128 GiB…
First, we needed to fix the cross build on Guix.
After the initial attempt at rumpdisk support for the Hurd it took (v2) some (v3) work (v4) to finally arrive at rumpdisk support for the Hurd, really, *really* (v5)
Sadly when actually using them, booting hangs:
start: pci.arbiter:
What did not really help is that upstream's rumpkernel archive was ridiculously large. We managed to work with upstream to remove unused bits from the archive. Upstream created a new archive that instead of 1.8 GiB (!) now “only” weighs 670 MiB.
Anyway, after a lot of building, rebuilding, and debugging and some more with kind help from upstream we finally got Rumpdisk and NetDDE to run in a Childhurd.

Now that the last (!) core-updates merge has finally happened (thanks everyone!), the recipe of installing Guix/Hurd has been much simpfilied. It goes something along these lines.
Install Guix/Linux on your X60,
Reserve a partition and format it for the Hurd:
mke2fs -o hurd -L hurd /dev/sdaX
In your config.scm, add some code to add GRUB menuentries for booting the Hurd, and mount the Hurd partition under /hurd:
(use-modules (srfi srfi-26)
(ice-9 match)
(ice-9 rdelim)
(ice-9 regex)
(gnu build file-systems))
(define %hurd-menuentry-regex
"menuentry \"(GNU with the Hurd[^{\"])\".*multiboot ([^ \n]) +([^\n])")
(define (text->hurd-menuentry text)
(let ((m (string-match %hurd-menuentry-regex text))
(label (match:substring m 1))
(kernel (match:substring m 2))
(arguments (match:substring m 3))
(arguments (string-split arguments #\space))
(root (find (cute string-prefix? "root=" <>) arguments))
(device-spec (match (string-split root #=)
(("root" device) device)))
(device (hurd-device-name->device-name device-spec))
(modules (list-matches "module ([^\n]*)" text))
(modules (map (cute match:substring <> 1) modules))
(modules (map (cute string-split <> #\space) modules)))
(menu-entry
(label label)
(device device)
(multiboot-kernel kernel)
(multiboot-arguments arguments)
(multiboot-modules modules))))
(define %hurd-menuentries-regex
"menuentry \"(GNU with the Hurd[^{\"])\" \{([^}]|[^\n]\})\n\}")
(define (grub.cfg->hurd-menuentries grub.cfg)
(let* ((entries (list-matches %hurd-menuentries-regex grub.cfg))
(entries (map (cute match:substring <> 0) entries)))
(map text->hurd-menuentry entries)))
(define (hurd-menuentries)
(let ((grub.cfg (with-input-from-file "/hurd/boot/grub/grub.cfg"
read-string)))
(grub.cfg->hurd-menuentries grub.cfg)))
...
(operating-system
...
(bootloader (bootloader-configuration
(bootloader grub-bootloader)
(targets '("/dev/sda"))
(menu-entries (hurd-menuentries))))
(file-systems (cons* (file-system
(device (file-system-label "guix"))
(mount-point "/")
(type "ext4"))
(file-system
(device (file-system-label "hurd"))
(mount-point "/hurd")
(type "ext2"))
%base-file-systems))
...)
Create a config.scm for your Hurd system. You can get inspiration from bare-hurd.tmpl and inherit from %hurd-default-operating-system. Use grub-minimal-bootloader and add a static-networking-service-type. Something like:
(use-modules (srfi srfi-1) (ice-9 match))
(use-modules (gnu) (gnu system hurd))
(operating-system
(inherit %hurd-default-operating-system)
(bootloader (bootloader-configuration
(bootloader grub-minimal-bootloader)
(targets '("/dev/sda"))))
(kernel-arguments '("noide"))
...
(services
(cons*
(service static-networking-service-type
(list %loopback-static-networking
(static-networking
(addresses
(list
(network-address
(device "eth0")
(value "192.168.178.37/24"))))
(routes
(list (network-route
(destination "default")
(gateway "192.168.178.1"))))
(requirement '())
(provision '(networking))
(name-servers '("192.168.178.1")))))
...)))
Install the Hurd. Assuming you have an ext2 filesystem mounted on /hurd, do something like:
guix system build --target=i586-pc-gnu vuurvlieg.hurd --verbosity=1
sudo -E guix system init --target=i586-pc-gnu --skip-checks \
vuurvlieg.hurd /hurd
sudo -E guix system reconfigure vuurvlieg.scm
Reboot and...
Hurray!
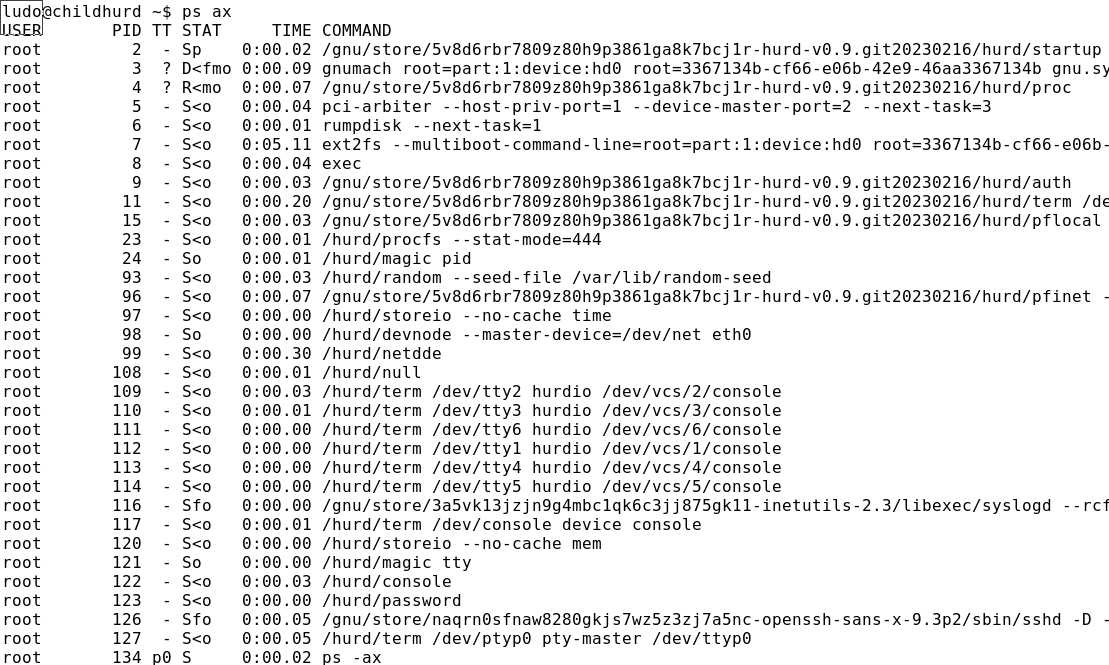
We now have Guix/Hurd running on Thinkpad.
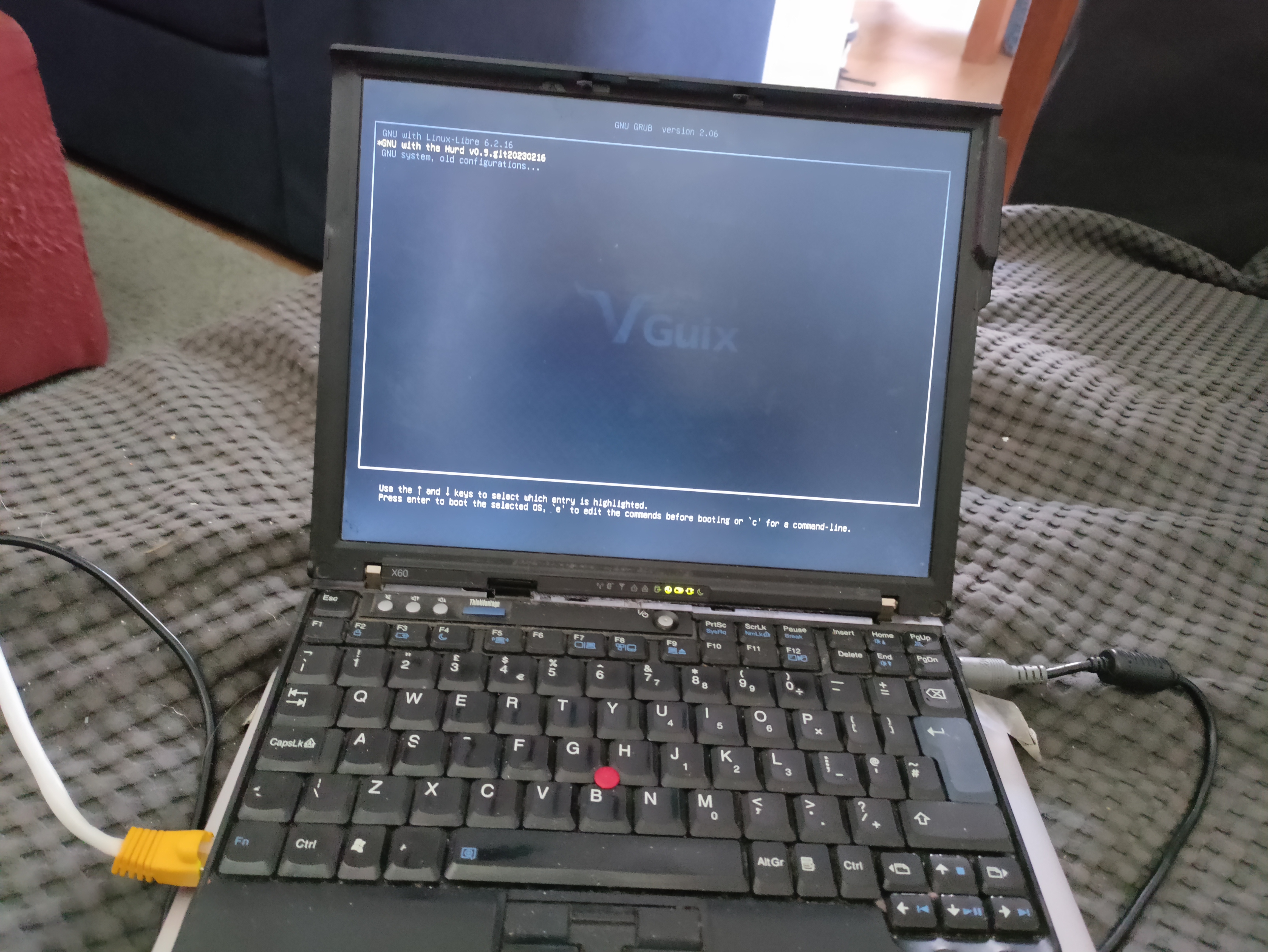
While the initial manual install on the X60 was an inspiring milestone, we can do better. As mentioned above, just recently the installer learnt about the Hurd, right after some smaller problems were addressed, like guix system init creating essential devices for the Hurd, not attempting to run a cross-built grub-install to install Grub, soft-coding the hard-coded part:1:device:wd0 root file-system, adding support for booting Guix/Hurd more than once.
To install Guix/Hurd, first, build a 32bit installation image and copy it to a USB stick:
guix system image --image-type=iso9660 --system=i686-linux gnu/system/install.scm
dd if=/gnu/store/cabba9e-image.iso of=/dev/sdX status=progress
sync
then boot it on a not-too-new machine that has wired internet (although installation over WIFI is possible, there is currently no WIFI support for the installed Hurd to use it). On the new Kernel page:
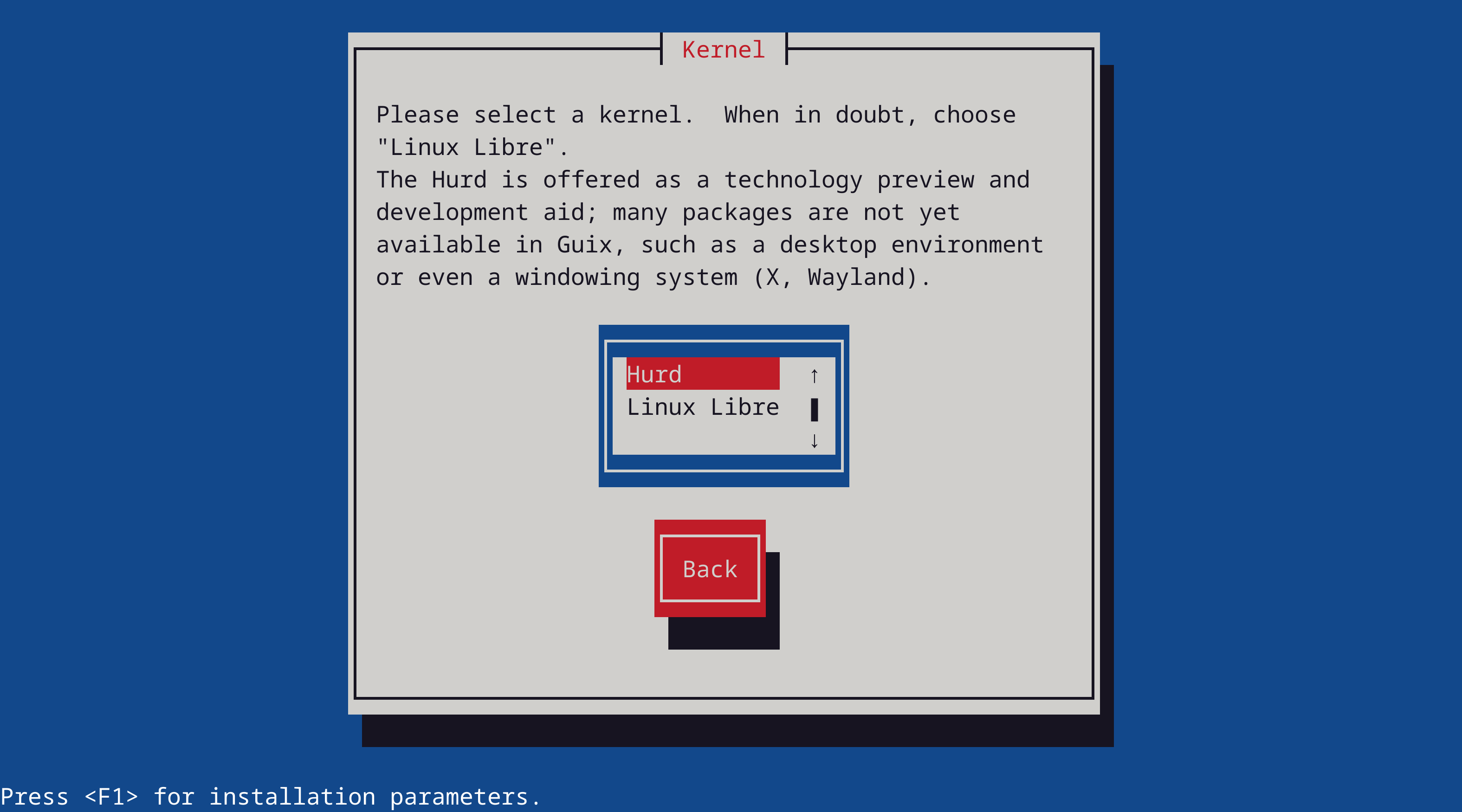
choose Hurd. Do not choose a desktop environment, that's not available yet. On the Network management page:
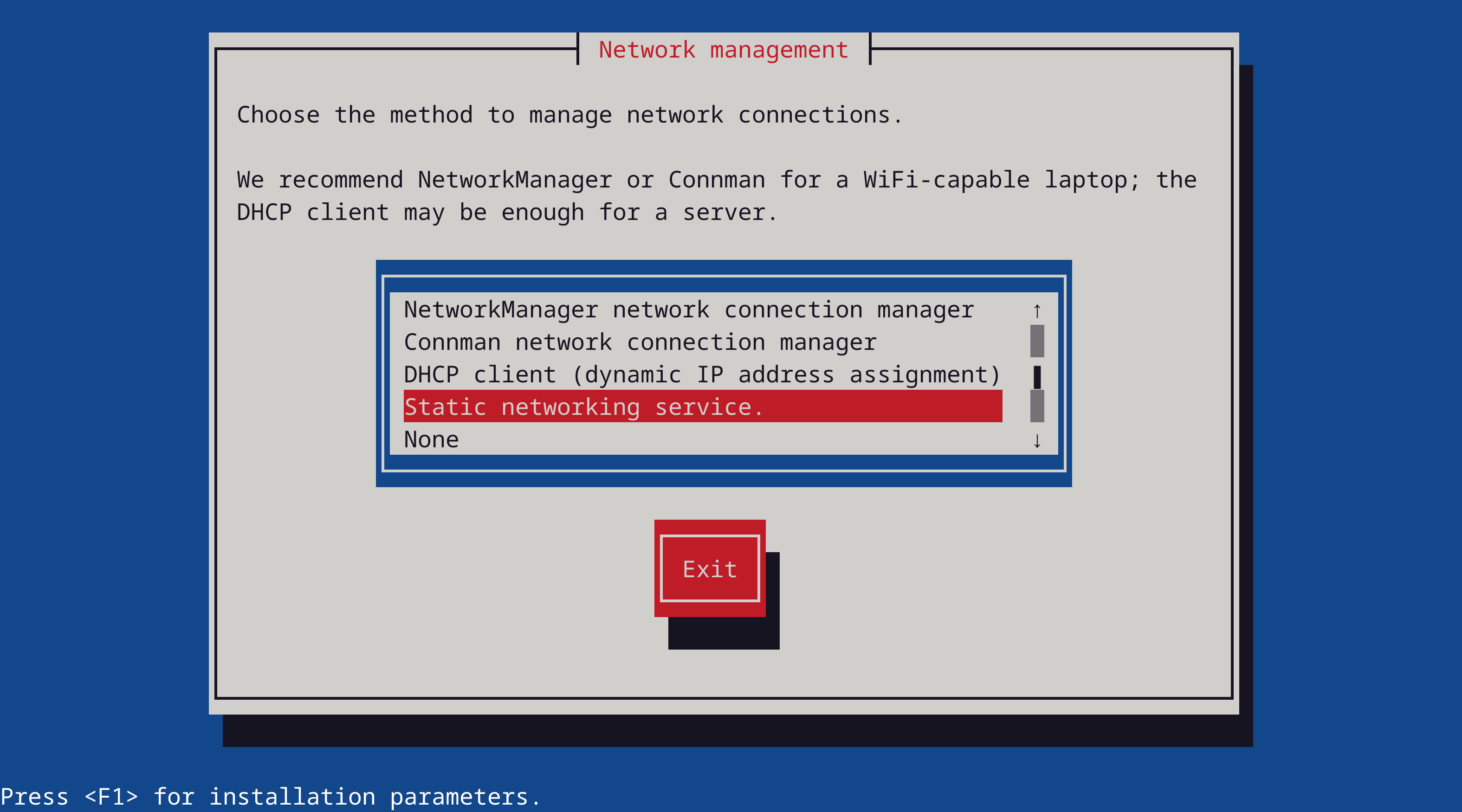
choose the new Static networking service. In the final Configuration file step, don't forget to edit:
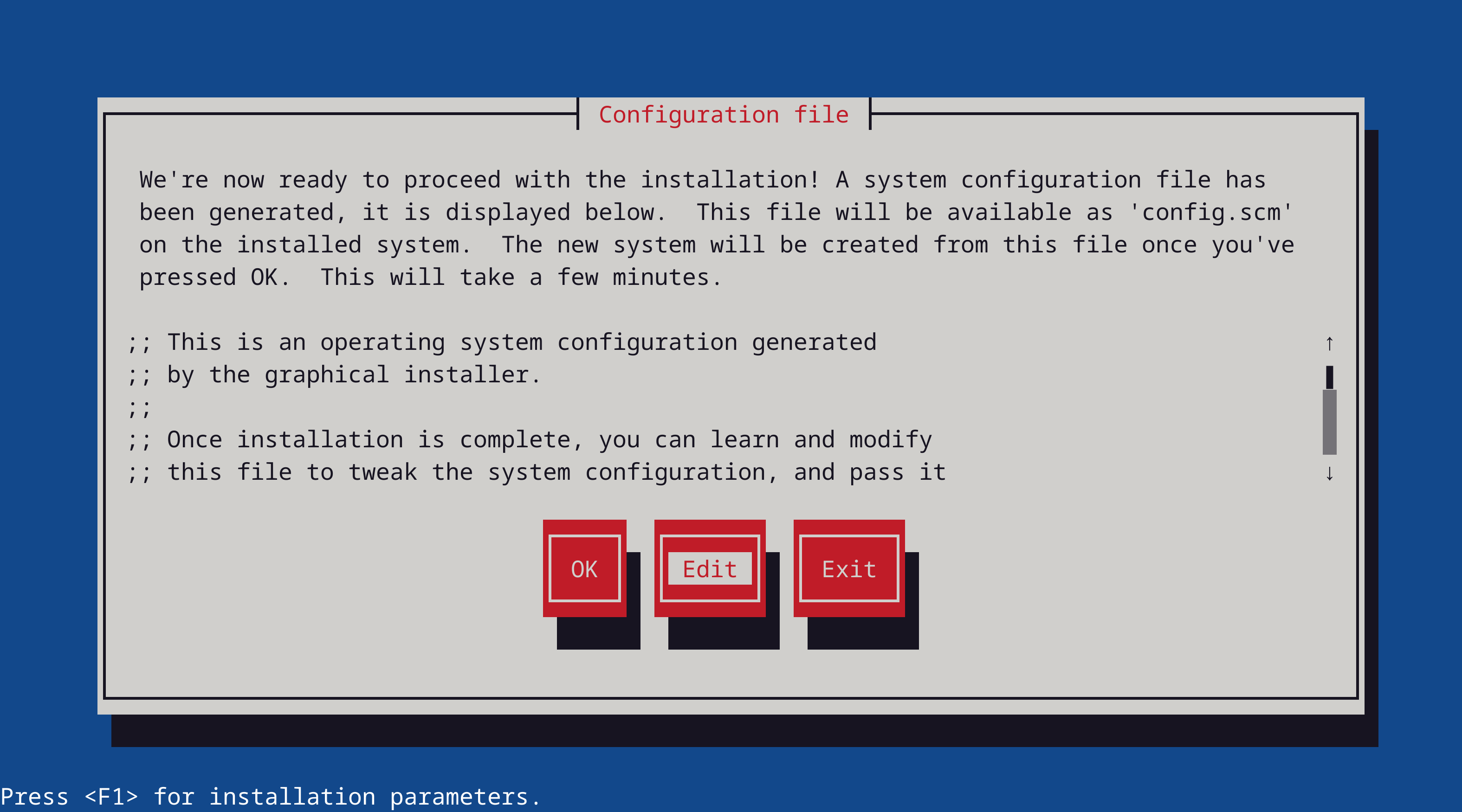
and fill-in your IP and GATEWAY:
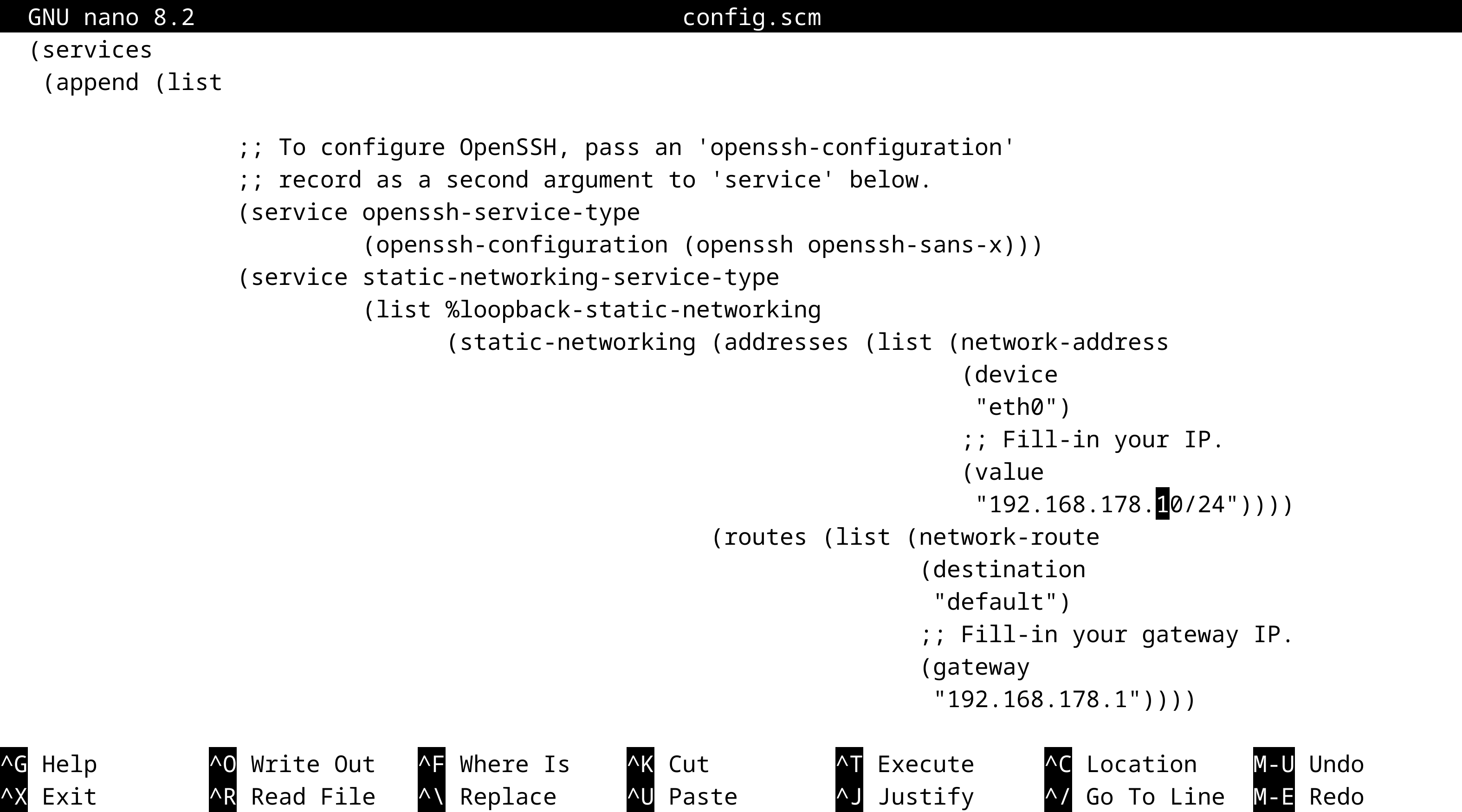
You may want to add some additional packages such as git-minimal from (gnu packages version-control) and sqlite from (gnu packages sqlite).
If you also intend to do Guix development on the Hurd—e.g., debugging and fixing native package builds—then you might want to include all dependencies to build the guix package, see the devel-hurd.tmpl for inspiration on how to do that. Note that any package you add must already have support for cross-building.
Good luck, and let us know if it works for you and on what kind of machine, or why it didn't!
In an earlier post we tried to answer the question “Why bother with the Hurd anyway?” An obvious question because it is all too easy to get discouraged, to downplay or underestimate the potential social impact of GNU and the Hurd.
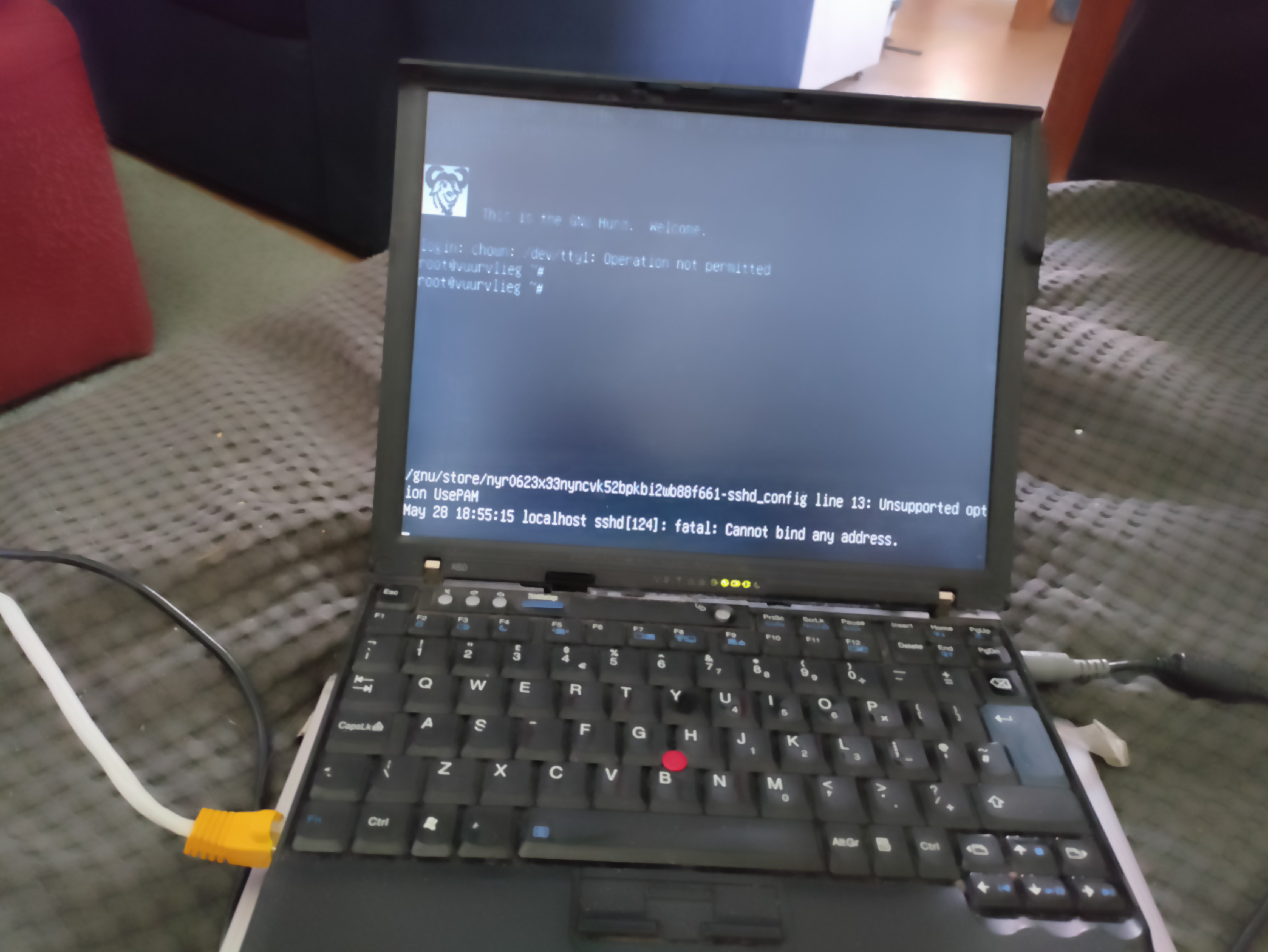
The most pressing problem currently is that the guix-daemon fails when invoking guix authenticate on the Hurd, which means that we cannot easily keep our substitutes up to date. guix pull is known to work but only by pulling from a local branch doing something like:
mkdir -p ~/src/guix
cd src/guix
git clone https://git.savannah.gnu.org/git/guix.git master
guix pull --url=~/src/guix/master
kinda like we did it in the old days. Sometimes it seems that guix does not grok the sqlite store database. This is needs to be resolved but as sqlite does read it this can be easily worked around by doing something like:
mv /var/guix/db/db.sqlite /var/guix/db/db.sqlite.orig
sqlite3 /var/guix/db/db.sqlite.orig .dump > /var/guix/db/db.sqlite.dump
sqlite3 -init /var/guix/db/db.sqlite.dump /var/guix/db/db.sqlite .quit
Also, the boot process still fails to handle an unclean root file system. Whenever the Hurd has suffered an unclean shutdown, cleaning it must currently be done manually, e.g., by booting from the installer USB stick.
Upstream now has decent support for 64bit (x86_64) albeit with more bugs and fewer packages. As mentioned in the overview we are now working to have that in Guix and have made some progress:
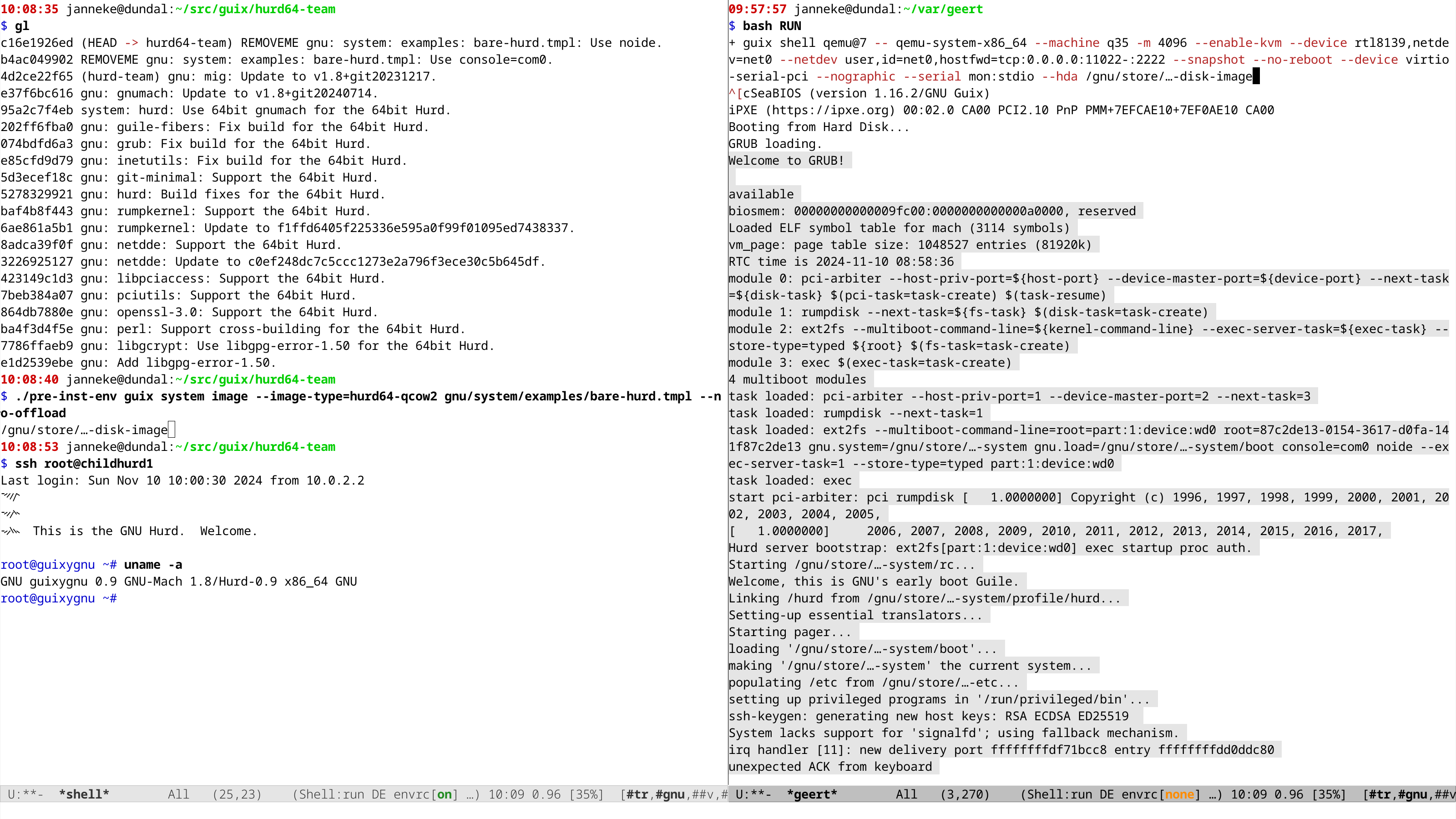
more on that in another post. Other interesting task for Guix include:
guix system reconfigure work on the Hurd,We tried to make Hurd development as easy and as pleasant as we could. As you have seen, things start to work pretty nicely and there is still plenty of work to do in Guix. In a way this is “merely packaging” the amazing work of others. Some of the real work that needs to be done and which is being discussed and is in progress right now includes:
All these tasks look daunting, and indeed that’s a lot of work ahead. But the development environment is certainly an advantage. Take an example: surely anyone who’s hacked on device drivers or file systems before would have loved to be able to GDB into the code, restart it, add breakpoints and so on—that’s exactly the experience that the Hurd offers. As for Guix, it will make it easy to test changes to the micro-kernel and to the Hurd servers, and that too has the potential to speed up development and make it a very nice experience.
Join #guix and #hurd on libera.chat or the mailing lists and get involved!
A lot has changed since the two last news from the GNU Boot project.
People involved in the GNU Boot project will be organizing a 100% free
software install party within a bigger event that also has a regular
install party. There will also be a presentation about 100% free
software in there. The event will be mainly in French.
More details are available in French and in English in the following
link:
https://lists.gnu.org/archive/html/help-guix/2024-11/msg00112.html
Many changes were made since the RC3 and since then we fixed an
important bug that prevented Trisquel from booting (If during the
Trisquel installation you chose "LVM2" and didn't encrypt the
storage, GNU Boot images with GRUB would not find the Trisquel
installation).
Because of that we decided to do a new RC4 (release candidate 4)
and to publish new GNU Boot images.
There are still some work needed before doing a 0.1 release as we want
to make it easier for less technical users to install and use GNU
Boot, but more and more of the project structure are getting in place
(website, manual, automatic tests, guix, good development procedures,
enabling build on all distributions, etc) which then makes it easier
to contribute.
We also decided to use Guix for more of the software components
we build, and since this is a big change, we will need people to
help more with testing.
The last announcement we made was "Nonfree software found in GNU Boot
releases again, many distros affected"[1].
Some people misunderstood it (maybe we could have been more clear):
the nonfree software that we found was code that GNU Boot didn't use,
so it was easy to remove and it didn't affect the supported devices in
any way.
Finding nonfree software in 100% free distribution is also common:
this is part of the work to ensure these distribution remains 100%
free.
The first time it happened in GNU Boot we publicized it to explain why
we were re-releasing some of the GNU Boot files as it could be very
scary if this happens without any public communication.
The second time we published a news about it mainly to help propagate
the information to the affected distributions and this is probably why
it was misunderstood: it was mainly targeted at GNU Boot users and
maintainers of the affected packages. We also contacted upstream and
some affected distributions directly as well but contacting everybody
takes a lot of time so having a news about it helps. At least Debian
and Trisquel fixed the issue but we still need to contact some
distributions.
After that, and probably thanks to the previous news, Leah Rowe
contacted us on one of the GNU Boot mailing lists[2] to notify us that
she also found additional similar nonfree software in GNU Boot.
So we confirmed that and promptly removed them and re-made again the
source release. And here again even if the work was delayed a bit,
this was fast to do and it doesn't affect the supported devices in any
way.
But we also need help contacting distributions again because one of
the issue she found is very serious because it affects many
distributions and also important devices that GNU Boot doesn't
support.
The ARM trusted firmware ships a nonfree hdcp.bin binary in its source
code. ARM trusted firmware is a dependency of u-boot that is used to
support many ARM computers in other distributions (like Guix, Debian,
etc).
As contacting affected distributions is a tedious task, we also need
help to propagate the information and contact them especially because
we don't know if Leah intend or not to do that work (so far she didn't
reply when asked twice about it), so it's probably up to the GNU Boot
community as a whole (which also includes its maintainers and readers
of this news) to help here.
The details are in the commit 343515aee7ef34695ac45830fad419d9562f9c15
("coreboot: blobs.list: arm-trusted-firmware: Remove RK3399 hdcp.bin
firmware.") in the GNU Boot source code[3].
[1]https://savannah.gnu.org/news/?id=10684
[2]https://lists.gnu.org/archive/html/gnuboot-patches/2024-10/msg00028.html
[3]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=343515aee7ef34695ac45830fad419d9562f9c15
Jordán (isf) has been contributing some Spanish translations of the
most important website pages (the landing, status and how to
contribute pages). This is important as it could help get more
contributors. These contributions also helped us improve the process
for accepting pseudonymous contributions and enabled us to fix issues.
The work on improving the website in general also continued. Many of
the website pages were reviewed and improved (there is a lot of work
there and mentioning it all would make the news way too long).
The website also now shows the git revision from which it is build and
we also helped the FSF fix some server configuration that created
issue with the deployment of the GNU Boot website (more details are in
the commit message[1]) by reporting the issue to them and testing the
fix.
Patches for making a manual are also being reviewed. While there isn't
much in the manual yet, it also enables to better organize the
documentation and it has the potential to make GNU Boot more
accessible to less technical people.
The next goals is to look how to merge part of the website inside the
manual and continue improving both the website and the manual.
[1]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=d1df672383f6eb8d4218fdef7fbe9ec5e41803e4
We now have the ability to verify the source code when downloading it
from git. This is important to avoid certain type of attacks and it
also enables to write code to automatically download, verify and build
the GNU Boot source code.
The source can be verified with the following command (it requires to
have Guix installed):
$ guix git authenticate $(git rev-parse HEAD) \
"E23C 26A5 DEEE C5FA 9CDD D57A 57BC 26A3 6871 16F6" \
-k origin/keyring
If the authentication works it will print a message like that:
guix git: successfully
authenticated commit 05c09293d9660ea1f26b5b705a089b466a0aa718
The 05c09293d9660ea1f26b5b705a089b466a0aa718 might be different in
your case.
The "E23C 26A5 DEEE C5FA 9CDD D57A 57BC 26A3 6871 16F6" part in the
command above is Adrien Bourmault (neox)'s GPG key.
How to use that will be documented more in depth in the upcoming GNU
Boot manual that is currently being reviewed. Its importance will also
be explained in more details for people not familiar with the security
issues it's meant to solve. Also note that we also welcome help for
reviewing patches.
The GNU Boot source code has a complex history. It is based on the
last fully free software releases of Libreboot. And the Libreboot
source code history is very complex.
We found some missing authorship information in some of the files that
come from Libreboot and so we started such information from the
various git repositories that were used at some point by Libreboot or
some of the projects it was based on.
To help with this task we also added a page on the GNU Boot website
(https://www.gnu.org/software/gnuboot/web/docs/history/) to track the
status of the reconstruction of the missing authorship and to document
the GNU Boot source code history.
GNU Boot is just a distribution and like most distributions, it tries
to collaborate with various upstream projects whenever possible.
Since GNU Boot relies on Guix, we improved the Guix documentation
directly to help people install Guix on Trisquel and Parabola. We also
helped Trisquel fix security issues in the Guix package by bug
reporting and testing fixes (some bugs still need to be fixed in
Parabola and Debian, and reporting issues upstream takes time).
Since we also advise to use PureOS or Trisquel to build GNU Boot we
also enabled people with Guix to produce PureOS or Trisquel chroots
with Debootstrap. This was done through contributions to Debootstrap,
and to the Guix Debootstrap package. We could then mention that in the
GNU Boot build documentation
(https://www.gnu.org/software/gnuboot/web/docs/build/) and added a
script (in contrib/start-guix-daemon.py) to support building GNU Boot
in chroots. However there are still issue with the build in chroots
that need to be fixed to producing all released files. Instructions on
how to do build in chroots is also lacking.
In addition we also added the ability to build GNU Boot with Trisquel
11 (aramo).
An apt-cacher-ng package was also contributed in Guix upstream as it
can then be used to speed-up one of the automatic tests used in GNU
Boot but the support for apt-cacher-ng was not integrated yet in GNU
Boot. Last year we also contributed a GRUB package in Guix but we
didn't have the occasion to use it yet. It will probably happen soon
though.
How to build GNU Boot has changed a lot since GNU Boot 0.1 RC3.
Before Guix could only be optionally used to build the website.
In addition to that, Guix is now integrated in the build system so we
can now rely on Guix packages to build GNU Boot images. This also
means that you need to install Guix to build GNU Boot images.
We currently use Guix packages to build some tests. We also build some
installation utilities for the I945 ThinkPads (ThinkPad X60, X60s,
X60T and T60) but we don't have documentation for less technical
people yet on how to use them. We also would need help for testing
these computers as we have no idea if they still work fine or which
fully free distributions still work on them in practice.
We now also support the './configure' and 'make' commands to build GNU
Boot but not yet the 'make install' command as to work we would need
to adapt many of the scripts that are used during the build to be
compatible with that.
There is also less visible work that was done, like cleaning up a lot
of code, adding tests for code quality, documenting a bit the GNU Boot
source code structure, and so on.
Work on making GNU Boot reproducible also started. See
https://reproducible-builds.org/ or
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reproducible_builds for more detail on
the issue.
We took an extremely strict approach and put the checksum of some of
the things we build directly into GNU Boot and verify it the checksum
during the compilation. This enables us to automatically detect
issues without having to do anything.
We started to enable that for easy things, and we also added the
infrastructure to also use that in Guix packages as well by validating
one of the packages we use during automatic testing.
However at one point this guix package stopped being
reproducible. Since we wanted to keep that code (especially as it was
showing a good example of how to do it), we fixed the bug instead of
removing the test.
This then helped us detect a very subtle and interesting bug in one of
the components we use for automatic tests.
The bug could not be caught during testing because some time
information stored inside the FAT32 file system has a granularity of a
day, and since all the testing happened the same day, it was caught
only later on.
This bug was then fixed and the details are in the fix[1]. A bug
report was also opened upstream because bugs were found in diffoscope
along the way[2]. We still need to do some testing though to
understand if the bug is in diffoscope or one of the underlying
libraries (libguestfs) and then to report the remaining bugs to the
distributions we used during this work.
We also made it easier to update the checksum in the Guix package. If
you package software with Guix, this change is also a good example of
how not to break the '--without-tests' option when you override the
tests in the package you contribute. The commit message[3] and the
change have more details and references on all that.
[1]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=4c3de49fbb3b43940b43f8fdccc8e51ee7df8f46
[2]https://salsa.debian.org/reproducible-builds/diffoscope/-/issues/390
[3]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=40fcb94e2f7ab1df8d320f78311e623f801d8602
WodeShengli reported a very important bug[1]: GNU Boot images with
GRUB can't find LVM2 partitions if the partition itself is not
encrypted. For instance if you have LVM2 and no encryption at all or
if the disk is encrypted and that on top you have LVM2, GNU Boot will
not find the partition.
Since this is an extremely serious usability issue (because images
with GRUB are supposed to work out of the box) we spent time to fix
it.
The issue was that the GRUB configuration we ship hardcoded the name
of the LVM volumes to try to boot from. Fixing it required to be able
loop over all the partitions being found, but we found no command to
do that in GRUB (which is probably why the LVM partition names were
hardcoded in the first place).
So we started adding GRUB command options to do that but while the
code worked fine, it didn't integrate in GRUB well. So we contacted
GRUB looking for help as we would have needed to upstream our command
option in GRUB anyway.
And we were told that GRUB already had a way to do what we were
looking for so we used that to fix the issue.
We also added tests that automatically download the Trisquel installer
and installs Trisquel with LVM2 and test if GNU Boot can boot the new
Trisquel installation[2].
While this test is skipped for 32bit computers, it is still good to
have as some people will run it. The test also paves the way to add
more tests that would enable us to improve further the GRUB
configuration without breaking the boot.
[1]https://savannah.gnu.org/bugs/index.php?65663
[2]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=860b00bf1e798d86c8bb2a70d77633599dfa1da2
[3]https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gnuboot.git/commit/?id=9cc02ddde1e164fabfbddc8bbd3832ef9468d92d

GNU Parallel 20241122 ('Ahoo Daryaei') has been released. It is available for download at: lbry://@GnuParallel:4
Quote of the month:
GNU parallel is so satisfying
-- James Coman @jcoman.bsky.social
New in this release:
News about GNU Parallel:
GNU Parallel - For people who live life in the parallel lane.
If you like GNU Parallel record a video testimonial: Say who you are, what you use GNU Parallel for, how it helps you, and what you like most about it. Include a command that uses GNU Parallel if you feel like it.
GNU Parallel is a shell tool for executing jobs in parallel using one or more computers. A job can be a single command or a small script that has to be run for each of the lines in the input. The typical input is a list of files, a list of hosts, a list of users, a list of URLs, or a list of tables. A job can also be a command that reads from a pipe. GNU Parallel can then split the input and pipe it into commands in parallel.
If you use xargs and tee today you will find GNU Parallel very easy to use as GNU Parallel is written to have the same options as xargs. If you write loops in shell, you will find GNU Parallel may be able to replace most of the loops and make them run faster by running several jobs in parallel. GNU Parallel can even replace nested loops.
GNU Parallel makes sure output from the commands is the same output as you would get had you run the commands sequentially. This makes it possible to use output from GNU Parallel as input for other programs.
For example you can run this to convert all jpeg files into png and gif files and have a progress bar:
parallel --bar convert {1} {1.}.{2} ::: *.jpg ::: png gif
Or you can generate big, medium, and small thumbnails of all jpeg files in sub dirs:
find . -name '*.jpg' |
parallel convert -geometry {2} {1} {1//}/thumb{2}_{1/} :::: - ::: 50 100 200
You can find more about GNU Parallel at: http://www.gnu.org/s/parallel/
You can install GNU Parallel in just 10 seconds with:
$ (wget -O - pi.dk/3 || lynx -source pi.dk/3 || curl pi.dk/3/ || \
fetch -o - http://pi.dk/3 ) > install.sh
$ sha1sum install.sh | grep 883c667e01eed62f975ad28b6d50e22a
12345678 883c667e 01eed62f 975ad28b 6d50e22a
$ md5sum install.sh | grep cc21b4c943fd03e93ae1ae49e28573c0
cc21b4c9 43fd03e9 3ae1ae49 e28573c0
$ sha512sum install.sh | grep ec113b49a54e705f86d51e784ebced224fdff3f52
79945d9d 250b42a4 2067bb00 99da012e c113b49a 54e705f8 6d51e784 ebced224
fdff3f52 ca588d64 e75f6033 61bd543f d631f592 2f87ceb2 ab034149 6df84a35
$ bash install.sh
Watch the intro video on http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL284C9FF2488BC6D1
Walk through the tutorial (man parallel_tutorial). Your command line will love you for it.
When using programs that use GNU Parallel to process data for publication please cite:
O. Tange (2018): GNU Parallel 2018, March 2018, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1146014.
If you like GNU Parallel:
If you use programs that use GNU Parallel for research:
If GNU Parallel saves you money:
GNU sql aims to give a simple, unified interface for accessing databases through all the different databases' command line clients. So far the focus has been on giving a common way to specify login information (protocol, username, password, hostname, and port number), size (database and table size), and running queries.
The database is addressed using a DBURL. If commands are left out you will get that database's interactive shell.
When using GNU SQL for a publication please cite:
O. Tange (2011): GNU SQL - A Command Line Tool for Accessing Different Databases Using DBURLs, ;login: The USENIX Magazine, April 2011:29-32.
GNU niceload slows down a program when the computer load average (or other system activity) is above a certain limit. When the limit is reached the program will be suspended for some time. If the limit is a soft limit the program will be allowed to run for short amounts of time before being suspended again. If the limit is a hard limit the program will only be allowed to run when the system is below the limit.
#floss #foss #gnu #gpl #linux #freedom #software #opensource #meme
♲ 𝕕𝕚𝕒𝕟𝕖𝕒 🏳️⚧️🦋 - 2024-11-23 01:47:33 GMT
Join the FSF and friends on Friday, November 22 from 12:00 to 15:00 EST (17:00 to 20:00 UTC) to help improve the Free Software Directory.
#linux #meme #gnu #install #software #os #advice #freedom #floss #foss
♲ anonymiss - 2024-11-22 03:21:08 GMT
Don't sell your soul to #Microsoft. Change from #Windows10 to #Linux and keep your old #computer running!
🐧💻🖥️👍
#gnu #linux #os #software #change #tux #windows #windows11 #meme #memes #nerd #advice #freedom #foss #floss