#malware
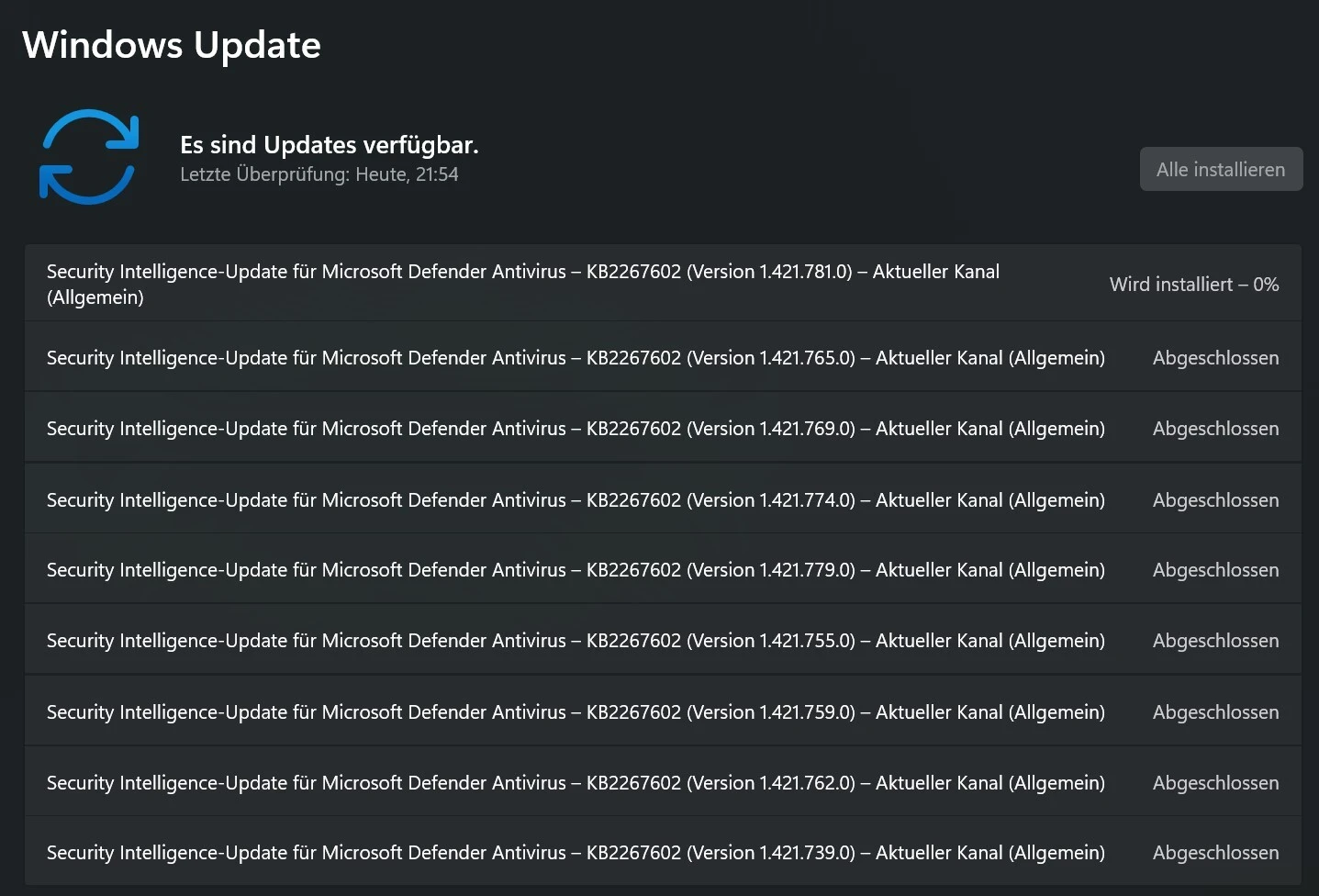
Ist der #Cyberkrieg schon ausgebrochen und das Ziel ist #Microsoft?
Mein Firmencomputer hat sich heute neunmal geupdatet. Ziel des Updates war immer die Virenabwehr von #WindowsSecurity. Ich vermute da läuft gerade eine heftige Schlacht im #Cyberspace mit einem mutierenden #Virus, sodass die #Signaturen ständig geupdatet werden müssen. Normal ist ein #Update pro Woche. Weiß jemand genaueres was da los ist?
#Cyberwar #Verteidigung #windows #update #Sicherheit #Software #Betriebssystem #Computer #Internet #online #virus #trojaner #schadsoftware #malware
[l] Hier ist noch eine Meldung in eine ähnliche Richtung:
Crypto-stealing malware posing as a meeting app targets Web3 pros
Kunden wundern sich immer, wieso ich nicht gewillt bin, irgendwelche versifften Meeting-Anwendungen zu installieren, und wenn sie auf ihrer ranzigen Software bestehen, dann bestehe ich auf dem ranzigen Webclient.
Freut mich sehr, dass das endlich mal jemand weaponized hat. War Zeit. Und könnte keine verdientere Gruppe treffen!
Why is proprietary #software so bad and full of #vulnerabilities?
The sales department probably doesn't know any better and only has its commission in mind and just sells the software, that's their job. I'm not so sure about the management, whether they are clueless or just think that no matter how bad the software is, we can earn even more money with support contracts. There are certainly a few clueless developers who are kept so busy that they barely manage to complete their tasks but have no time for quality assurance. However, a large part of the developers will realize what is being played and then either change jobs after 2 years if it becomes unbearable or try to justify the quality of the software according to the motto it is a feature and not a bug. Ultimately, the only option left to cybersecurity is to secure vulnerable software with supposedly better security software. Bugs are not fixed unless public pressure is so strong that it is unavoidable and with one fixed bug, three new ones are installed. The supposedly secure security software all too often turns out to be snake oil, which only brings further security risks, which then have to be secured by further security software and you find yourself in a never-ending cascade, which becomes ever more dangerous and expensive but brings no security gain. There is even a technical term for this, called security theater. At the end of the day, all the management wants to say in its press release is that the hackers were diabolical criminals and probably had state support, but that the company had done everything it could to defend itself with the latest security software. The starting position is therefore clear. There is money to be made from security vulnerabilities and proper security means a lot of work. Economic considerations are therefore made here, according to which quality assurance can be saved because the customer can find and report the errors after all.
I'm pretty sure I'm not the smartest or the best developer, but I've figured it out and I'm always surprised that I often meet colleagues who are very confident about cybersecurity in the company because there is security training every year. I don't see any possibility of developing secure software at all under capitalism because profit is always valued higher than security.
#developer #management #economy #capitalism #profit #finance #security #cybersecurity #bug #fail #system #problem #hack #hacker #malware
[l] Old and busted: Sophos gibt zu, ihren Kunden Malware installiert zu haben.
New hotness: Palo Alto gibt zu, ihren Kunden Malware installiert zu haben.
As a means to test an AV/EDR bypass tool, these endpoints had older versions of Cortex XDR agents installed. Unbeknownst to the threat actor, we were able to access these rogue endpoints.
We also discovered a series of toolkits and other files belonging to the threat actor on the system, which included the bypass tool. We successfully traced and identified posts related to the sale of this specific tool on cybercrime forums like XSS and Exploit.
[l] Ich bin ja mit meinem Blog nicht nur ein Sammler von Verschwörungstheorien, ich bin auch eine Cassandra in der IT-Security-Branche. Seit Jahrzehnten sage ich, dass Antiviren die Angriffsoberfläche nicht senken sondern erhöhen, dass das ein falsches Versprechen von Sicherheit ist, dass sich Leute von "Metriken" blenden lassen, die von voreingenommener Seite produziert und vorgelegt werden, und dann falsche Entscheidungen treffen.
Bei Verschwörungstheorien beobachte ich immer begeistert, wie jahrelanges Wegleugnen eines Tages spontan umspringt, entweder zu "haben wir doch schon immer gewusst" (hat sich aber nie im Handeln niedergeschlagen und wurde die ganze Zeit nach Kräften geleugnet!), oder, noch schlimmer, zu "haben wir doch schon immer gesagt" (eine glatte Lüge).
Umso erfreulicher für mich in letzter Zeit, wie sich bei Kernthemen von mir langsam herauskristallisiert, dass wir uns diesem Kipppunkt nähern.
Heise-Kommentar: Sophos und der gebrochene Schwur. Was ist der gebrochene Schwur? Dass Sophos Malware an ihre Kunden verteilt hat, um angebliche chinesische Hacker auszuspionieren, die ihre kaputte Sophos-Software genutzt haben, um Sophos-Kunden anzugreifen. Hier mein Kommentar zu der Sophos-Nummer, als die ganz frisch war. Jürgen Schmidt, Chef von Heise Security, dazu:
Sie haben selbst Spionage-Software entwickelt und die gezielt auf Systemen von Kunden platziert, um diese auszuforschen. Das war eigentlich ein ungeschriebenes Gesetz der Branche: Wir entwickeln keine Malware und insbesondere setzen wir sie nicht ein, um unsere Kunden auszuspionieren.
Ich würde noch einen Schritt weiter gehen und sagen: Das war schon immer Malware. Gut, ich habe da Einblicke, die vielleicht nicht jeder hat. Ich weiß, wie so "Antiviren" funktionieren, und was für Methoden die verwenden, um Kernel-Calls zu hooken und ihren Code in Prozesse zu injecten. Das ist genau das, was eine Verhaltens-Anomalie-Erkennung sofort als Malware flaggen würde. Daher haben die Antiviren Whitelists drin, um sich nicht gegenseitig zu flaggen, und warnen explizit davor, nur eine "Endpoint Security" zur Zeit zu installieren, und deshalb schaltet Norton erstmal den MS Defender aus. Der würde nämlich alle Alarmglocken zünden, wenn Norton tut, was Norton halt so tut. Norton hier als Stellvertreter für alle Antiviren.
Wenn man das weiß, dann wird spontan klar: Das war schon immer Malware, die sich Rechte rausnimmt, die man im System niemandem zugestehen sollte, schon gar nicht Vertriebsgetriebenen Firmen wie Antivirenherstellern.
Dieses ungeschriebene Gesetz, das Jürgen hier zitiert, das gab es noch nie. Das war schon immer ein Trust Me I Know What I'm Doing, und genau wie bei Wurstproduktion will der Konsument da gar nicht so genau hingucken, weil er weiß: Wenn er wüsste, was da passiert, könnte er das Produkt nicht mehr konsumieren.Ich für meinen Teil finde auch nicht glaubwürdig, dass Sophos diesen Übersprung dazu, mit krimineller Energie Malware an ihre Kunden auszuliefern und deren Systeme absichtlich weiter zu gefährden, nur in diesem einen Fall gegen die fiesen Chinesen einsetzt. Kriminelle Energie mateiralisiert sich nicht über Nacht. So viel kriminelle Energie muss man über Jahre hegen und pflegen. Nur eine durch und durch unvertrauenswürdige Firma würde auch nur erwägen, solche Methoden einzusetzen.Überlegt euch auch mal, wie verbogen deren moralischer Kompass sein muss, damit sie das auch noch für eine gute Idee, das öffentlich zuzugeben und sich damit als Helden zu feiern zu versuchen.Sophos steht hier als Stellvertreter für alle Antiviren. Glaubt mal gar nicht, dass irgendeiner von denen vertrauenswürdig ist.Hier ist noch ein Kipppunkt-Indikator. Ein anderer Heise-Kommentator pflichtet mir bei, dass es ungefährlicher ist, für Entdecker von Sicherheitslücken, die im Darknet zu verkloppen als sie dem Verursacher zu melden. Ich persönlich habe seit mindestens 20 Jahren keine Sicherheitslücken mehr initiativ-gemeldet oder auch nur gesucht. Ich suche Sicherheitslücken, wenn mich der Hersteller dafür bezahlt. Wenn ich über eine stolpere, melde ich die nur wenn es sich um freie Software handelt. An Bug Bounty-Programmen nehme ich nicht teil.Die Lobbyisten der Industrie haben die Rahmenbedingungen so gesetzt, dass ich auch allen anderen nur raten kann, es mir gleich zu tun. Anderes aktuelles Beispiel in dem Kontext waren die polnischen Eisenbahnhacker auf dem letzten CCC-Kongress.
Die mussten sich inzwischen vor Gericht einer Klage dieser Firma stellen. Ich bewundere deren Heldenmut, aber hätte ich nicht gemacht. Da wäre ich Trump-Wähler und würde den ganzen Apparat herunterbrennen sehen wollen, bevor ich wieder mitzuhelfen bereit wäre. Dankt CDU und FDP.
Auch da scheint sich inzwischen die Erkenntnis breit zu machen, dass ich die ganze Zeit Recht hatte, und es gibt jetzt den Versuch eines Reförmchens. Ich glaube es, wenn ich es sehe.
Wenn man bedenkt, wie viel billiger und besser wir das alles hätten haben können, wenn die Leute gleich auf mich hören würden. Aber Plan B greift auch: Aus Schmerzen lernen. In diesem Sinne: Geht ihr mal alle in die Cloud und macht Blockchain, IoT und "KI". Wir sehen uns in 10 Jahren wieder und weinen gemeinsam dem verbrannten Geld hinterher.
#fefebot #fdp #cdu #trump #ccc #malware
Hundreds of #code #libraries posted to #NPM try to #install #malware on dev machines
The malicious packages have names that are similar to legitimate ones for the Puppeteer and Bignum.js code libraries and for various libraries for working with #cryptocurrency.
Dependency hell 👎👿
#software #problem #development #library #dependency #security #cybersecurity #news #cybercrime #attack
[l] Ich erzähle ja seit Jahrzehnten inzwischen, dass Schlangenöl nicht nur keine Sicherheit gegen Malware bringt, sondern im Gegenteil die Angriffsoberfläche vergrößert und daher unter dem Strich sogar kontraproduktiv ist.
Wisst ihr, wer das jetzt auch sagt? Sophos.
For years, it's been an inconvenient truth within the cybersecurity industry that the network security devices sold to protect customers from spies and cybercriminals are, themselves, often the machines those intruders hack to gain access to their targets. Again and again, vulnerabilities in “perimeter” devices like firewalls and VPN appliances have become footholds for sophisticated hackers trying to break into the very systems those appliances were designed to safeguard.
Ach. Ach was. Wartet, das war noch nicht Sophos. Das war die Einleitung von Wired.
Wieso sagen die Leute das eigentlich immer erst, wenn es nicht mehr zu leugnen ist?
Sophos versucht es natürlich anders zu spinnen. Sie sind hier die glorreichen Helden, die gegen die verruchten fiesen Chinesen "zurückhacken". Da werden sich aber die üblichen Kompetenzgranaten in Deutschland freuen, die meinen Vortrag dazu noch nicht gesehen haben.
The company went as far as discreetly installing its own “implants” on the Chinese hackers' Sophos devices to monitor and preempt their attempts at exploiting its firewalls.
Das ist selbstverständlich illegal, und zwar sowohl unter chinesischen wie auch unter britischem oder EU-Recht. Sophos gibt hier also unumwunden Straftaten zu. Das könnt ihr ja mal mit eurer Einkaufsabteilung besprechen, wenn die bei Sophos eingekauft haben.
Aber mal abgesehen davon. Was fand Sophos denn da?
In the process, Sophos analysts identified a series of hacking campaigns that had started with indiscriminate mass exploitation of its products but eventually became more stealthy and targeted, hitting nuclear energy suppliers and regulators, military targets including a military hospital, telecoms, government and intelligence agencies, and the airport of one national capital. While most of the targets—which Sophos declined to identify in greater detail—were in South and Southeast Asia, a smaller number were in Europe, the Middle East, and the United States.
Das ist schön ausweichend formuliert, daher lasst es mich noch mal betonen. Alle diese Organisationen wurden über Sophos-Pfusch-Produkte angegriffen. Wenn die auf mich gehört und kein Schlangenöl gekauft hätten, wären die Chinesen auf dem Weg nicht reingekommen.
Sophos says it’s telling that story now [...] to break the cybersecurity industry's awkward silence around the larger issue of vulnerabilities in security appliances serving as entry points for hackers.
Absolut an der Zeit. Hätten sie auch 20 Jahre früher machen können. Am besten direkt auf ihre Produkte eine fette Warnung aufdrucken! Wer das hier kauft, öffnet den Chinesen eine Hintertür in sein Netz.
Ist jetzt natürliche in bisschen ungerecht, so auf Sophos herumzuhauen. Die sind ja nur einer der Player, und der erste, der ein bisschen Anflüge von Ehrlichkeit zeigt in der Beziehung.
In just the past year, for instance, flaws in security products from other vendors including Ivanti, Fortinet, Cisco, and Palo Alto have all been exploited in mass hacking or targeted intrusion campaigns.
No shit.
Bleibt mir nur eines zu sagen:
TOLD YOU SO. (via)
US Immigration Agency Contract with Spyware Company Poses Risk to Rights
Systems Needed to Hold Industry, Governments to International Standards
https://www.hrw.org/news/2024/10/17/us-immigration-agency-contract-spyware-company-poses-risk-rights
United States Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), a US government agency linked to human rights abuses, has contracted services from the Israeli spyware company Paragon, according to a government contracting website. Wired magazine first reported on the US$2 million contract, which the agency signed with Paragon in September.\
\
The contract summary doesn't name a specific product, but Paragon is best known for Graphite, a spyware tool that, like its competitor Pegasus, can bypass the encryption of many smartphones and give access to the data inside. In 2022, the New York Times reported that the US Drug Enforcement Agency was also using Paragon’s software. That same year, the Federal Bureau of Investigations sought to deploy Pegasus, developed and sold by NSO Group, but backed out in response to public pressure. One week after the Wired article was published, the contract summary was updated with a stop work order, but the current state of Paragon’s work for ICE is unclear.
#spyware #ice #immigration-and-customs-enforcement #us-government #usa #paragon-software #graphite #human-rights #human-rights-watch #hrw #fbi #pegasus #nso #israel #malware
U'khand CM Dhami reviews cyber #security infra after #malware #attack
...
#Dhami also directed the officials to conduct a security #audit of the 'State Data Centre' and the #website.
The question is rather why the security of the software was not sufficiently audited in advance and whether this is the right software at all if it is susceptible to such attacks?
Chinese# botnet infects 260,000 #SOHO #routers, IP cameras with #malware
#news #cybersecurity #cybercrime #iot #infection #software #security #fail #problem #china
Ukraine bans #Telegram on #military, govt devices over #security risks
Ukrainian officials representing the country's Security Service and the General Staff of the Armed Forces also warned that #Russia "actively" uses Telegram for cyberattacks, #phishing, #malware distribution, and coordinating #missile strikes.
This is not a revolutionary realization. It would be interesting to know whether the Russian secret service has also infiltrated servers in order to expose users and monitor them specifically.
#news #cybersecurity #messenger #communication #internet #spy #problem #surveillance #Ukraine #warfare #attack #cybercrime #war #fake #disinformation #propaganda
#Malware says hooray 😱
Source: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/excel-blog/python-in-excel-available-now/ba-p/4240212
#Python in #Excel is now generally available for #Windows users of #Microsoft 365 Business and Enterprise.







